Liang Yi1, Zhengguo Shi2,3, Liangcheng Tan2, Chenglong Deng4,5
1. State Key Laboratory of Marine Geology, Tongji University, Shanghai China.
2. State Key Laboratory of Loess and Quaternary Geology, Institute of Earth Environment, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Xi’an China.
3. CAS Center for Excellence in Tibetan Plateau Earth Sciences, Beijing, China.
4. State Key Laboratory of Lithospheric Evolution, Institute of Geology and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China.
5.University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing, China
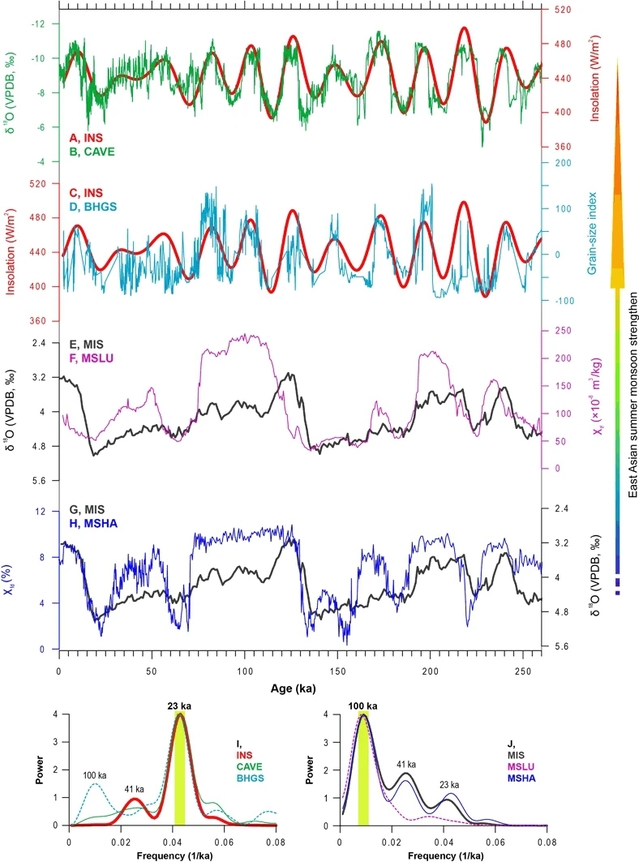
Abstract:We conducted a statistical study to characterize the nonlinear response of the East Asian summer monsoon (EASM) to its potential forcing factors over the last 260 ka on orbital timescales. We find that both variation in solar insolation and global ice volume were responsible for the nonlinear forcing of orbital-scale monsoonal variations, accounting for ~80% of the total variance. Specifically, EASM records with dominated precession variance exhibit a more sensitive response to changes in solar insolation during intervals of enhanced monsoon strength, but are less sensitive during intervals of reduced monsoon strength. In the case of global ice volume with 100-ka variance, this difference is not one of sensitivity but rather a difference in baseline conditions, such as the relative areas of land and sea which affected the land–sea thermal gradient. We therefore suggest that EASM records with dominated precession variance recorded the signal of a shift in the location of the Inter-tropical Convergence Zone, and the associated changes in the incidence of torrential rainfall; while for proxies with dominated 100-ka variance, it recorded changes in the land–sea thermal gradient via its effects on non-torrential precipitation.
Full article:https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s00382-017-3743-5